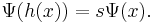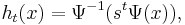Schröder's equation
Schröder's equation,[1][2][3] named after Ernst Schröder, is a functional equation with one independent variable: given the function h(x), find the function Ψ(x) such that
Schroeder's equation is an eigenvalue equation for the composition operator Ch, which sends a function f(x) to f(h(x)).
If a is a fixed point of h(x), meaning h(a) = a, then Ψ(a)=0 (or ∞). Thus, provided Ψ(a) is finite and Ψ' (a) does not vanish or diverge, the eigenvalue s is given by s = h' (a).
Contents |
Functional significance
For a=0, if h is analytic on the unit disk, fixes 0, and 0<|h'(0)|<1, then Koenigs showed in 1884 that there is an analytic (non-trivial) f satisfying Schroeder's equation. This is one of the first steps in a long line of theorems fruitful for understanding composition operators on analytic function spaces.
Equations such as Schröder's are suitable to encoding self-similarity, and have thus been extensively utilized in studies of nonlinear dynamics (often referred to colloquially as chaos theory). It is also used in studies of turbulence, as well as the renormalization group.[4][5]
An equivalent transpose form of Schröder's equation for the inverse Φ = Ψ−1 of Schröder's conjugacy function is h(Φ(y)) = Φ(cy). The change of variables α(x) = log(Ψ(x))/log(s) (cf. superfunction) further converts Schröder's equation to the older Abel equation, α(h(x)) = α(x) + 1. Similarly, the change of variables Ψ(x) = log(φ(x)) converts Schröder's equation to Böttcher's equation, φ(h(x)) = (φ(x))s.
The n-th power of a solution of Schröder's equation provides a solution of Schröder's equation with eigenvalue sn, instead. In the same vein, for an invertible solution Ψ(x) of Schröder's equation, the (non-invertible) function Ψ(x) k(logΨ(x)) is also a solution, for any periodic function k(x) with period log(s). All solutions of Schröder's equation are related in this manner.
Solutions
Schröder's equation was solved analytically in the cases of:
- A superattracting fixed point (h' (a) = 0) by L. E. Böttcher (1904),[6]
- An attracting but not superattracting fixed point (|h' (a)| < 1 ) by Gabriel Koenigs (1884).[7][8]
There are a good number of particular solutions dating back to Schröder's original 1870 paper.[1]
The series expansion around a fixed point and the relevant convergence properties of the solution for the resulting orbit and its analyticity properties are cogently summarized by Szekeres.[9] Several of the solutions are furnished in terms of asymptotic series.
Applications
It is used to analyse discrete dynamical systems by finding a new coordinate system in which the system (orbit) generated by h(x) looks simpler.
More specifically, a system for which a discrete unit time step amounts to x → h(x), can have its smooth orbit (or flow) reconstructed from the solution of the above Schröder's equation, its conjugacy equation.
That is, h(x) = Ψ−1(s Ψ(x)) ≡ h1(x).
In general, all of its functional iterates (its regular iteration group, cf. iterated function) are provided by the orbit
for t real — not necessarily positive or integer. (Thus a full continuous group.) The set of hn(x) , i.e., of all positive integer iterates of h(x) (semigroup) is called the splinter (or Picard sequence) of h(x).
However, all iterates (fractional, infinitesimal, or negative) of h(x) are likewise specified through the coordinate transformation Ψ(x) determined to solve Schröder's equation: a holographic continuous interpolation of the initial discrete recursion x → h(x) has been constructed;[10] in effect, the entire orbit.
For instance, the functional square root is h½(x) = Ψ−1 (s1/2 Ψ(x) ), so that h½( h½(x) ) = h (x), and so on.
For example,[11] special cases of the logistic map such as the chaotic case h(x) = 4x(1 − x) were already worked out by Schröder in his original paper[1] (cf. p. 306), Ψ(x) = arcsin2(√x), s = 4, and hence ht(x) = sin2(2t arcsin(√x)).
In fact, this solution is seen to result as motion dictated by a sequence of switchback potentials,[12] V(x) ∝ x(x − 1) (nπ + arcsin √x )2, a generic feature of continuous iterates effected by Schröder's equation.
A nonchaotic case he also illustrated with his method, h(x) = 2x(1 − x), yields Ψ(x) = −½ ln(1−2x), and hence ht(x) = −½((1−2x)2t−1).
References
- ^ a b c Schröder, Ernst (1870). "Ueber iterirte Functionen". Math. Ann. 3 (2): 296–322. doi:10.1007/BF01443992.
- ^ Carleson, Lennart; Gamelin, Theodore W. (1993). Complex Dynamics. Textbook series: Universitext: Tracts in Mathematics. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97942-5.
- ^ Kuczma, Marek (1968). Functional equations in a single variable. Monografie Matematyczne. Warszawa: PWN – Polish Scientific Publishers.
- ^ Gell-Mann, M.; Low, F.E. (1954). "Quantum Electrodynamics at Small Distances". Physical Review 95 (5): 1300–1312. Bibcode 1954PhRv...95.1300G. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.95.1300.
- ^ Curtright, T.L.; Zachos, C.K. (March 2011). "Renormalization Group Functional Equations". Physical Review D 83 (6): 065019. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.83.065019.
- ^ Böttcher, L. E. (1904). "The principal laws of convergence of iterates and their application to analysis". Izv. Kazan. Fiz.-Mat. Obshch. 14: 155–234.
- ^ Koenigs, G. (1884). "Recherches sur les intégrales de certaines équations fonctionelles". Annales de l'École Normale Supérieure 1 (3, Supplément): 3–41. http://www.numdam.org/numdam-bin/fitem?id=ASENS_1884_3_1__S3_0.
- ^ Erdös, P.; Jabotinsky, E. (1960). "On Analytic Iteration". Journal d'Analyse Mathématique 8 (1): 361–376. doi:10.1007/BF02786856.
- ^ Szekeres, G. (1958). "Regular iteration of real and complex functions". Acta Mathematica 100 (3–4): 361–376. doi:10.1007/BF02559539.
- ^ Curtright, T.L.; Zachos, C.K. (2009). "Evolution Profiles and Functional Equations". Journal of Physics A 42 (48): 485208. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/42/48/485208.
- ^ Curtright, T.L. Evolution surfaces and Schröder functional methods.
- ^ Curtright, T.L.; Zachos, C.K. (2010). "Chaotic Maps, Hamiltonian Flows, and Holographic Methods". Journal of Physics A 43 (44): 445101. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/43/44/445101.